In the world of research, qualitative data holds significant value as it provides a detailed, in-depth perspective on the subject matter. Unlike quantitative data that answers ‘how much’ or ‘how many,’ qualitative data delves into the ‘why’ and ‘how,’ thereby revealing insights that numbers alone cannot capture.
Table of contents
- Understanding the Significance of Transcription in Qualitative Research
- Core Transcription Techniques for Qualitative Data
- Leveraging Technology in Transcription
- Transcription as a Tool for In-Depth Analysis
- Best Practices for Effective Transcription
- The Future of Transcription in Qualitative Research
The process of transcription plays a pivotal role in preserving the richness of qualitative data. Transcription acts as the bridge between the raw audio or video data collected from interviews, focus groups, or observations, and the written text that researchers analyse. The accuracy of this transcription process directly impacts the richness and reliability of the qualitative data.
Effective transcription techniques are indeed crucial for capturing nuances and ensuring a comprehensive qualitative data analysis. The following sections will further delve into this relationship, offering practical advice for enhancing transcription and thereby improving the overall quality and depth of qualitative research.
Understanding the Significance of Transcription in Qualitative Research

Qualitative research is a methodology that focuses on understanding human behaviour, attitudes, and experiences in a naturalistic setting. It can bring forth a thorough understanding of complex phenomena that quantitative research might not fully capture.
Definition and Importance of Qualitative Research

Qualitative research aims to inspect the ‘why’ and ‘how’ behind human interactions and behaviours. It enables the researcher to delve deeper, capturing the nuances and contexts that might otherwise remain unnoticed in quantitative research. The richness of information obtained through qualitative research is often instrumental in forming hypotheses and theories.
Role of Transcription in Qualitative Data Collection
Transcription is the process of converting spoken language into written form, a crucial step in qualitative data analysis. Without accurate transcription, valuable insights could be lost, eroding the richness of the qualitative data. It helps in ensuring the data’s credibility and reliability, allowing researchers to revisit and analyse again the data multiple times.
Challenges of Accurately Capturing Verbal and Non-Verbal Cues
- Capturing non-verbal cues such as tone, pauses, and inflections can be challenging but are often crucial for interpreting the data accurately in qualitative research.
- Verbatim transcriptions can be tedious and time-consuming, especially when dealing with lengthy interviews or focus groups.
- Transcribing colloquial language or jargon might pose a challenge in ensuring the transcription’s accuracy and comprehensibility.
Understanding these aspects can help researchers navigate the complex process of transcription, thereby enhancing the depth and quality of their qualitative data analysis.
Core Transcription Techniques for Qualitative Data
Understanding the different transcription techniques used in qualitative research can significantly improve the quality of data and the subsequent analysis.
Verbatim vs. Non-verbatim Transcription: Pros and Cons
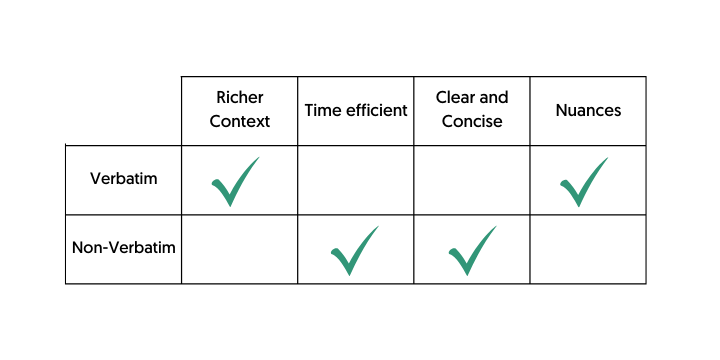
- Verbatim Transcription: This detailed method involves transcribing every utterance, including fillers, repetitions, and false starts, offering a comprehensive account of the dialogue. While it provides a richer context, it can be time-consuming and might sometimes clutter the data with unnecessary information.
- Non-verbatim Transcription: This approach omits certain details like fillers and repetitions, focusing on the core content. Although quicker and easier to read, it might miss out on subtle nuances that could be vital in qualitative analysis.
Importance of capturing non-verbal cues (pauses, laughter, intonation)
- Non-verbal cues provide deeper insights into a respondent’s emotions and attitudes, adding a layer of depth to the data.
- Pauses could indicate hesitation or deep thought, laughter could reveal discomfort or joy, and changes in tone or intonation could help interpret the respondent’s feelings.
- Capturing these cues can be challenging but are integral to a comprehensive qualitative analysis.
Time-stamping and its relevance in qualitative analysis
- Time-stamping involves marking the points in the transcript that correspond to the specific time in the audio or video recording.
- It enables easy referencing and tracking of data, improving the efficiency of the analysis process.
- Time-stamping also aids in accurately associating non-verbal cues and contextual details with the corresponding dialogue, thereby enhancing the richness of the data.
While there are multiple transcription techniques, choosing the right one depends on the research requirements. A balanced approach that captures the necessary details without overwhelming the data is often most effective in qualitative research.
Open-Ended Questions in Qualitative Research: Strategies, Examples, and Best Practices
Read NowLeveraging Technology in Transcription

Overview of Technological Tools Aiding Transcription:
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): ASR is a technology that converts spoken language into written text, significantly speeding up the transcription process. However, it’s important to note that ASR may struggle with understanding accents, colloquialisms, and background noise, requiring human review for accuracy.
- AI-Driven Transcription Software: AI-powered software can transcribe audio and video files with impressive accuracy and speed. These tools often come with features such as speaker identification and timestamping, which can be invaluable in qualitative research.
Balancing Technology and Human Judgment for Accuracy:
While technology offers speed and convenience, it cannot completely replace human judgment, particularly in determining context, interpreting nuances, and recognising emotional cues. Combining automated transcription with human review allows for greater precision and reliability in the qualitative data analysis process.
Ethical Considerations in Automated Transcription:
The use of automated transcription raises certain ethical issues that researchers must consider. Privacy concerns are paramount, as sensitive information may be processed and stored by third-party software. It’s crucial to ensure that any transcription tool used complies with data protection regulations and maintains a high standard of data security. In addition, researchers should remain transparent about their use of automated transcription with interviewees or participants, obtaining their consent whenever necessary.

3 ways automated speech recognition (ASR) can foster digital inclusion
Read NowTranscription as a Tool for In-Depth Analysis
In the context of qualitative research, transcription serves as a powerful tool for in-depth analysis. It lays the groundwork for various analytical methods, aiding researchers in uncovering intricate patterns and themes.
How Transcription Facilitates Thematic Analysis and Coding
- Thematic analysis, a widely used method in qualitative research, involves identifying, analysing, and reporting patterns within the data. Transcripts provide the raw material for this process, enabling researchers to comb through the data with a fine-toothed comb, identifying recurring themes and categories.
- Coding, an essential step in thematic analysis, involves assigning labels to data segments that represent distinct themes or patterns. An accurate and detailed transcript facilitates efficient coding, enabling the researcher to highlight and categorise key sections of the data.
Enhancing Interpretive Phenomenological Analysis Through Detailed Transcripts
- Interpretive phenomenological analysis (IPA) seeks to understand the lived experiences of individuals and how they make sense of these experiences. A detailed transcript, capturing the nuances of language, emotion, and thought processes, can significantly enhance the richness and depth of IPA.
- Verbatim transcripts, in particular, can help capture the uniqueness of individual experiences, enabling researchers to delve deeper into the subjective world of the participants.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Transcription in Qualitative Research
- A study exploring the lived experiences of cancer survivors benefitted immensely from transcription. Verbatim transcription captured the emotional undertones and personal expressions of the participants, revealing deep insights into their coping mechanisms and emotional resilience.
- In a qualitative study exploring customer behaviour in a retail environment, transcription played a critical role. The transcribed customer interviews provided a wealth of data that was then coded and categorised, revealing emerging patterns in customer preferences and shopping behaviour.
Precise transcription not only aids in data organisation but also adds depth to the data interpretation, making it an essential tool in qualitative research. The right transcription techniques can unveil hidden subtleties, leading to a more sophisticated understanding of the research subject.
Best Practices for Effective Transcription
Adhering to best practices can make the process of transcription more efficient and yield higher quality results. Here are some tips for preparing and conducting interviews, guidelines for transcribers, and insights on training and skill development.

Tips for Preparing and Conducting Interviews to Ease Transcription
- Prepare a script: Having a prepared set of questions for your interview can ensure a focused and organized discussion. This not only streamlines the conversation but also simplifies the subsequent transcription process.
- Use quality recording equipment: High-quality audio is critical for effective transcription. Using good recording equipment reduces the risk of audio issues such as background noise or low volume, making the transcription process smoother and more accurate.
- Clarify responses during the interview: If a response is unclear during the interview, don’t hesitate to ask for clarification. This can save time during the transcription process and ensure the accuracy of the data.
Guidelines for Transcribers: Accuracy, Consistency, and Confidentiality
- Accuracy: Transcribers should aim for the highest level of accuracy, transcribing exactly what is said without adding, omitting, or altering words. Even seemingly minor errors can significantly distort the meaning of the data.
- Consistency: Transcribers should be consistent in their transcription style, following the same conventions throughout the document. This makes the data easier to analyze and interpret.
- Confidentiality: Transcribers often handle sensitive data. They must respect the confidentiality of the information and adhere strictly to privacy practices and regulations.
Training and Skill Development for Transcribers
- Develop strong typing skills: Fast and accurate typing is a crucial skill for efficient transcription. Regular practice can help improve typing speed and accuracy.
- Improve listening skills: Good transcribers are also good listeners. Improving listening skills can help transcribers catch nuances and subtleties that may be missed otherwise.
- Learn to use transcription software: There are many transcription tools available that can streamline the process. Transcribers should familiarize themselves with these tools and learn to utilize them effectively.
Remember, transcription is not just about converting spoken words into written text. It’s about capturing the essence of the conversation, the emotions, and the context. It’s a crucial part of qualitative research that requires skill, patience, and dedication.
The Future of Transcription in Qualitative Research
Looking ahead, transcription is set to play an increasingly integral role in qualitative data analysis. Developments in technology are paving the way for more efficient, precise, and nuanced transcription techniques, promising exciting potentials for qualitative research.

Emerging Trends and Future Prospects in Transcription Technology
- Automation and AI: With the advent of advanced speech recognition technology, we are moving towards more automated transcription processes. While these technologies can increase efficiency, it’s important to note that they are not yet capable of capturing the nuances that a human transcriber can.
- Integration with Analytics Tools: Future transcription tools may offer seamless integration with qualitative data analysis software, facilitating immediate and insightful analysis of transcribed data.
The Evolving Role of Transcribers in the Digital Age
- Despite advances in technology, the role of human transcribers remains critical. Their ability to capture emotional nuances, contextual cues, and subtle meanings distinguishes them from AI and automated systems.
- As technology evolves, so does the role of transcribers. They may find themselves working in tandem with AI, leveraging the speed of automated transcription while adding the human touch of nuanced understanding.
Anticipating the Changing Needs of Qualitative Data Analysis
- As qualitative research methodologies evolve and diversify, so too will the requirements for transcription. Future trends may include more flexible transcription styles, allowing for the capture of non-verbal cues and the dynamics of conversation.
- Researchers and organisations will need to stay abreast of these trends, adapting their transcription practices to meet the changing needs of qualitative data analysis.
Transcription is not merely a mechanical process, but a critical tool in the quest to unlock the full value of qualitative data. With the right techniques and an emphasis on capturing nuances, transcription can provide rich, detailed data, serving as a bedrock for insightful analysis. In an era of rapidly evolving technology, the importance of skilled, dedicated transcribers cannot be overstated.

Get a customized offer
Request a quote for your transcription needs
For researchers and organisations seeking to maximise the value of their qualitative data, investing in advanced transcription techniques and training is a logical step. With the right skills and tools, transcribers can transform raw conversation into a gold mine of insights, helping drive informed decision-making and innovative research conclusions. Don’t let the nuances of your data slip away, elevate your qualitative research with effective transcription !
